6263. Dwarf tower
Little Vasya is
playing a game called “Dwarf Tower”. In this game, there are n different
items that can be equipped on a character – a dwarf. All items are numbered
from 1 to n. Vasya wants to obtain item number 1.
There are two ways
to obtain items:
·
Buy an item: the i-th item costs ci
coins.
· Craft an item: there
are m different crafting
recipes in the game. To craft a new item, you need to give two other distinct
items.
Help Vasya spend as
little money as possible to get item number 1.
Input. The first line
contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 104, 0 ≤ m ≤ 105) – the number of different items
and the number of crafting recipes.
The second line
contains n integers ci (0 ≤ ci ≤ 109) – the costs of the
items.
Each of the
following m lines describes a recipe. Each line contains three distinct
integers ai, xi, yi, where ai is the item that
can be crafted from items xi and yi (1 ≤ ai, xi, yi
≤ n, ai ≠ xi,
xi ≠ yi, yi ≠ ai).
Output. Print one integer –
the minimum amount of money that needs to be spent.
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
5 3 5 0 1 2 5 5 2 3 4 2 3 1 4 5 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
3 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 |
2 |
SOLUTION
greedy
Algorithm
analysis
Build a graph in the form of an adjacency list g, where g[i] contains pairs of numbers (j, a) such that items i and j can be combined to produce
item a: (i, j) → a.
Let cost be an array initially
containing the purchase costs of the items (cost[i] = ci). By the end of the algorithm cost[i] will store
the minimum amount of money required to obtain item i.
Initially, all items are considered unprocessed (used[i] = 0).
While there is at least one unprocessed item:
·
Find the item a with the smallest cost;
·
Apply all rules listed in g[a];
·
Mark item a as processed: used[a] = 0;
For each
rule (a, b) → to
from g[a] we recompute
cost[to]
= min(cost[to], cost[a]
+ cost[b])
Example
Consider
the first test. There are 5 items with the following purchase costs:
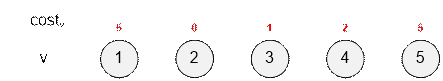
There are
three item crafting rules. Let’s build an adjacency list based on them.
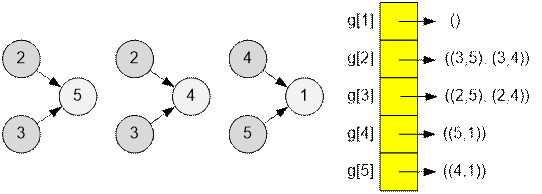
Item 2 has
the smallest cost: cost[2] = 0. Apply all rules involving item 2,
namely those listed in g[2]. After
that, mark item 2 as processed.
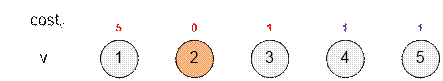
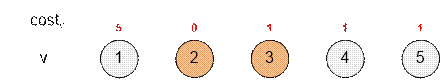
The next
unprocessed item with the smallest cost is 3. Apply the rules listed in g[3]. The
costs of the items do not change in this step.
Next, the
unprocessed item with the smallest cost becomes item 4. Apply the rule from g[4].
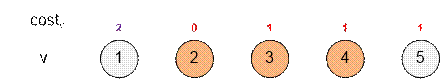
In the
subsequent operations, the costs of the items do not change. Thus, the minimum
cost to obtain item 1 is 2.
Algorithm implementation
Declare the arrays. Declare an adjacency list g,
which will contain the item crafting rules.
vector<int> cost, used;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g;
Read the input data. Initialize the arrays.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
g.resize(n
+ 1);
cost.resize(n
+ 1);
used.resize(n
+ 1);
Read the
purchase costs of the items.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &cost[i]);
Read the
item crafting rules and build an adjacency list based on them.
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &x, &y);
g[x].push_back(make_pair(y, a));
g[y].push_back(make_pair(x, a));
}
Perform n iterations.
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
In each iteration, among the unprocessed items, find
the one with the smallest cost. Let this be the item with number a.
mn = 2e9; a = -1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!used[i] && cost[i] < mn)
{
mn = cost[i];
a = i;
}
Mark item a as processed.
used[a] = 1;
Iterate through all rules involving item a.
for (auto x : g[a])
{
b = x.first;
to = x.second; // (a, b) -> to
if (cost[a] + cost[b] < cost[to]) cost[to] = cost[a] + cost[b];
}
}
Print the
minimum amount of money required to purchase the first item.
printf("%d\n", cost[1]);
Python implementation
In Python,
inf is a special value representing infinity. It is available in
the math module, which must be imported to use it.
from math import inf
Read the input data.
n, m = map(int, input().split())
cost = [0] + list(map(int, input().split()))
Initialize the lists.
used = [False] * (n + 1)
g = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
Read the
item crafting rules and build an adjacency list based on them.
for _ in range(m):
a,
x, y = map(int, input().split())
g[x].append((y, a))
g[y].append((x, a))
Perform n iterations.
for k in range(n):
In each iteration, among the unprocessed items, find
the one with the smallest cost. Let this be the item with number a.
mn
= inf
a
= -1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if not used[i] and cost[i] < mn:
mn = cost[i]
a = i
Mark item a as processed.
used[a] = True
Iterate through all rules involving item a.
for
b, to in g[a]:
if cost[a] +
cost[b] < cost[to]:
cost[to] = cost[a] + cost[b]
Print the
minimum amount of money required to purchase the first item.
print(cost[1])